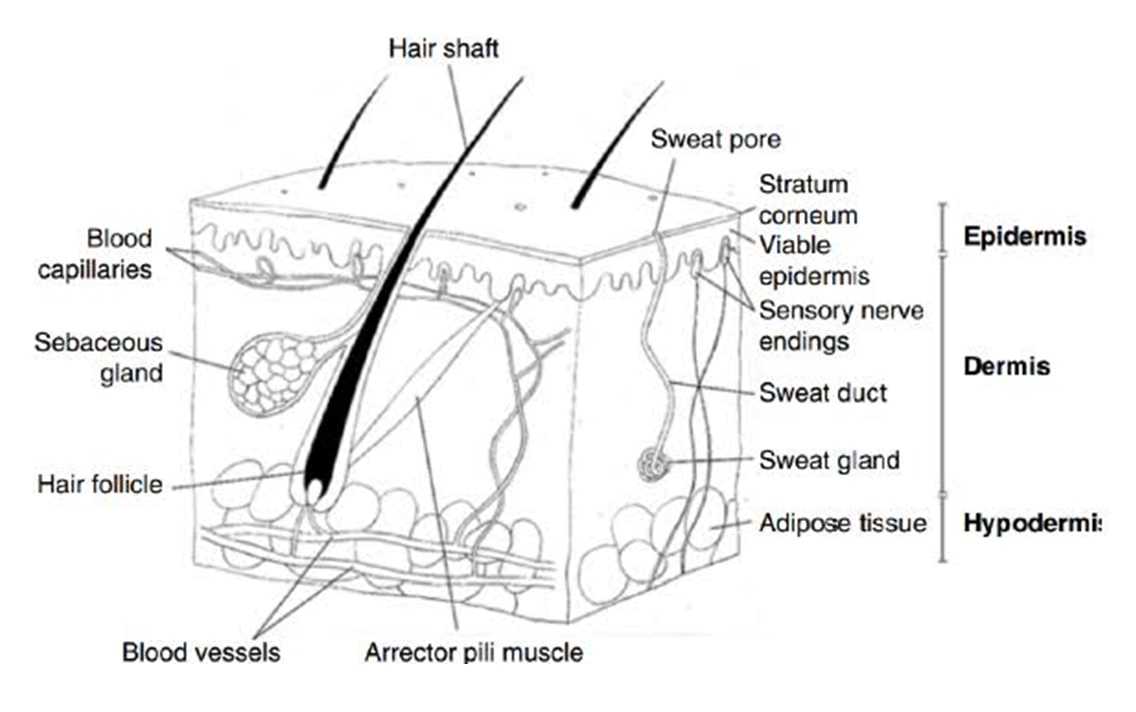
SKIN BASIC STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF SKIN
• Skin is a continuous organ,sensoryorgan,and heaviest
• Its pH is about 5-6.5,acidicmedium.As it is acidic it stops the entry of microorganisms.
• It acts as a barrier for internal organs.
Types of skin:
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Sub-cutaneous
4. Skin appendages
1) EPIDERMIS:
• It is the outer most layer of skin
• Multilayered
• It has different thickness 0.8 -hands and feet , 0.06-eyelids
Types of epidermis:
Stratum corneum:
it contains dead keratinized cells ,10micrometers,contains columnar highly organized in ventricular column .
relative humidity 15-20%.
when creams are applied the stratum corneum is highly hydrated where evaporation of water takes place.
when the skin is dried it forms brittle and breakdown called as chapped lips.
Stratum corneum is divided into 2 types:
• Horny pads: it is 40 times thicker than that of membranous stratum corneum.
- Weight bearing and fraction.
• Membranous stratum corneum: it is flexible ,impermeable in nature.
Responsible for percutaneous absorption of chemical substances & also has a tendency of shedding of stratum corneum is about 0.5-1 kg.
Stratum lucidum:
It is a poorly staining hyaline zone of palms of hand and soles of feet.
Non-nucleated.
Thin ,translucent layer.
Stratum granulosum:
It is a granular layer .
It has a keratin composed of keratinized cells called keratinocytes, which produces keratohyalinegranules ,which are responsible for basic staining.
Keratinocytes have an intense biochemical activity.
Stratum spinosum:
It is also called as prickle cell layer.
As basal cells moves upwards the cells of these become flattened and nuclei shrinks ,which result in prickle cells.
Prickle cells along with adjacent cells & cytoplasm forming inter connected bridge called as “desmosomes” & responsible for integrity of epidermis.
Stratum germinatum:
This layer contains basal cells.
6 micrometer in thickness,nucleated and columnar
The cells that are produced are melanocytes ,which secrete melanin(pigment)
This melanin helps in pigmentation and protection against the radiations.
2) DERMIS:
It is present in between layers of epidermis & subcutaneous.
It comprises of dense nature or matter of structural proteins such as elastin, reticulin & collagen.
These are dispersed in semigel matrix of mucopolysaccharides as ground substance , which gives elasticity.
It is 0.2-0.3 micrometer in thickness.
3) SUBCUTANEOUS:
This layer is present below dermis.
The sheet of fat is comprised of areolar tissue.
That is superficial fascia ,which is attached to dermis.
In this layer large arteries and veins are present.
4) SKIN APPENDAGES:
This contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands,sweatglands.
This is present all over the body except lips ,palms,soles etc.
Sebaceous glands: it contains sebum comprised of fats, proteins, inorganic salts, cholesterol .
Sweat glands:
It is divided into 2 types.
• Eccrine glands: these are large ,coiledglands,of 100-200micrometers thickness
They are also called as “salty glands” as they secrete very dilute solution of salt.
It controls heat and temperature.
• Apocrine glands: these are present in anogenital areas such as nipples ,arm pits .
Essential fatty acids are:
Lineolicacid ,arachidonic acid which act as barrier function.
FUNCTIONS OF SKIN:
• It protects internal organs.
• It regulates body temperature
• It regulates blood pressure
• It protects against external stimuli such as radiation ,heat,cold.
• It helps in excretion of metabolic wastes
• It helps in containiment of body fluids
• Proteinase enzyme(anti-inflammatory action in cell injury)
• Metabolises VitD-D3, calcitriole
• Free fatty acids-shows fungicidal and bactericidal activity.
• Responsible for biochemical synthesis.
• Reception of stimuli.